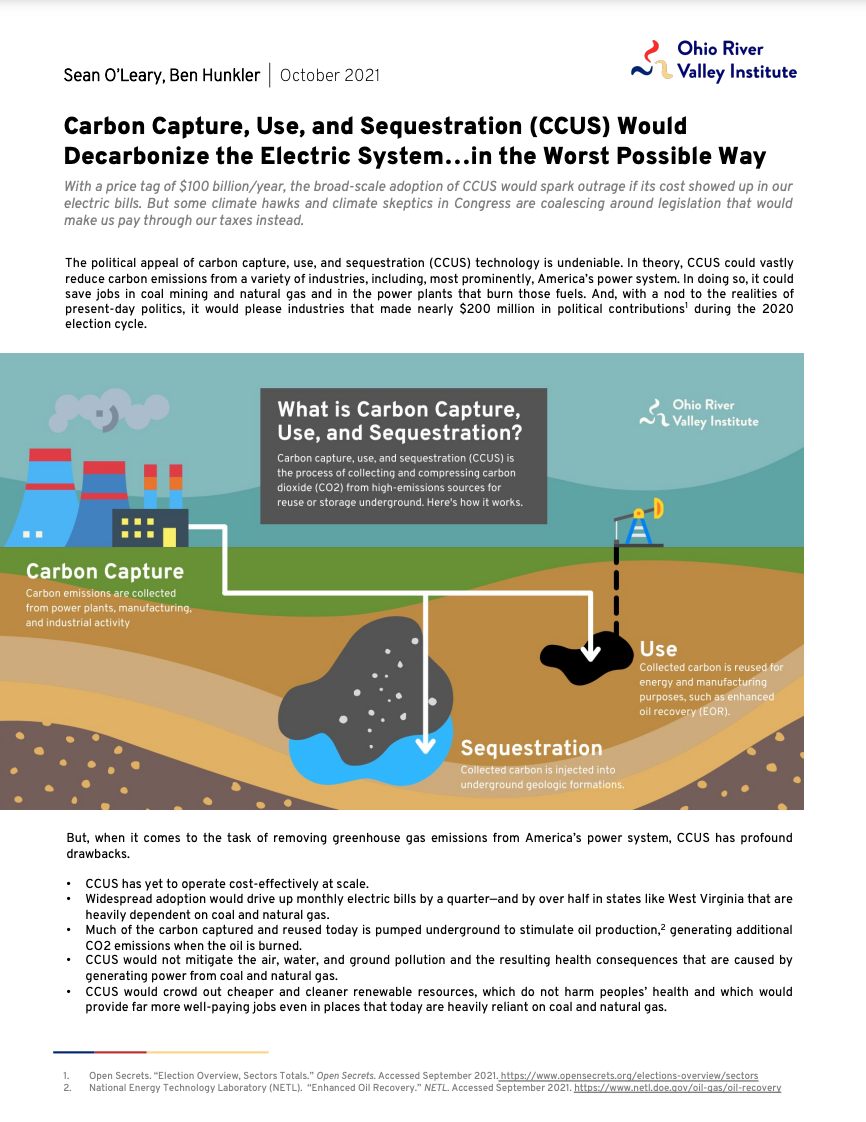
Hydrogen & Carbon Capture

Blue hydrogen and carbon capture are false climate solutions & economic boondoggles.
Expensive, unproven hydrogen and carbon capture technologies harm communities, cost billions, and do little to reduce climate-warming emissions, research shows.
Photo: John E. Amos coal-fired power plant in Winfield, WV. Wikimedia Commons, 2018.
“Oil and gas executives want our region to invest in costly, unproven blue hydrogen and carbon capture technologies to bail out their industries, which increasingly can’t compete with clean, low-cost alternatives.”
Reports:
More resources:
Governor Shapiro’s “Lightning Plan”: What HB500 Means for Hydrogen
Pennsylvania Governor Josh Shapiro’s proposal for a hydrogen tax credit addresses some of the worst aspects of the existing tax credit but the tax credit still rewards polluters and leaves itself vulnerable to changes that could render it moot, unenforceable, or...
The Tri-State CCS Hub: Reading Between the Lines
Last month, a representative for Tenaska — the company seeking to build the Tri-State Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) Hub — testified before the Ohio House Natural Resource Committee in support of House Bill 170. If passed and signed into law, this bill would...
Ohio House Bill 170 and Senate Bill 136: What You Should Know
Legislators in Ohio seek to establish a regulatory framework for the long-term, geologic storage of carbon dioxide in order to provide the clarity needed to attract developers to the state. But, HB170 and SB136 go far beyond this simple goal. If passed, these two...
ARCH2: It’s Time for Our Leaders to Start Asking Tough Questions
The Appalachian Hydrogen Hub (ARCH2) was always a questionable prospect. Since 2021, the Ohio River Valley Institute has asserted that carbon capture and blue hydrogen, the technologies underpinning what later became the hub, are prohibitively expensive and only...
A Month from Hell
Key Points Northern Appalachia has, for a decade and a half, premised its economic development strategies on a strategic triad of natural gas, petrochemicals, and most recently hydrogen. Natural gas expansion has proven itself incapable of delivering on promises of...
The Carbon Implications of Ammonia Production
The US is on the verge of an ammonia ‘boom,’ which could expand fracking and incentivize risky carbon storage infrastructure. But as with any boom, industrial expansion will eventually bring a bust. At least 37 new projects have been proposed around the country which...
The Uncertain Ammonia Industry, Present & Future
Layers of uncertainty around new ammonia markets and the ability of new projects to scale...
Statement on the Approval of West Virginia’s Class VI Primacy Application
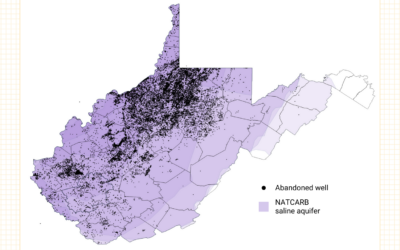
Abandoned Wells Could Wreak Havoc for Carbon Storage in West Virginia
Tens of thousands of abandoned wells overlay West Virginia’s prospective carbon storage reservoirs, risking leakage.